Pan-India, the ability to construct modern structures is often obstructed by the inability to contemporize the local traditional systems of construction eventually resulting in
eye-sores set in heritage infused surroundings.
eye-sores set in heritage infused surroundings.
Set in a small town Wai in Maharashtra, a settlement study carried out in groups of six established the day-to-day effects of the local river, the native population’s interaction with it through temples, ghats and bridges, and its ignorance of the centuries-old built heritage. an in-depth sectional analysis of the unique regional construction systems provide an insight to the genius of the architects in the use of local materials individually and in tandem with each other.
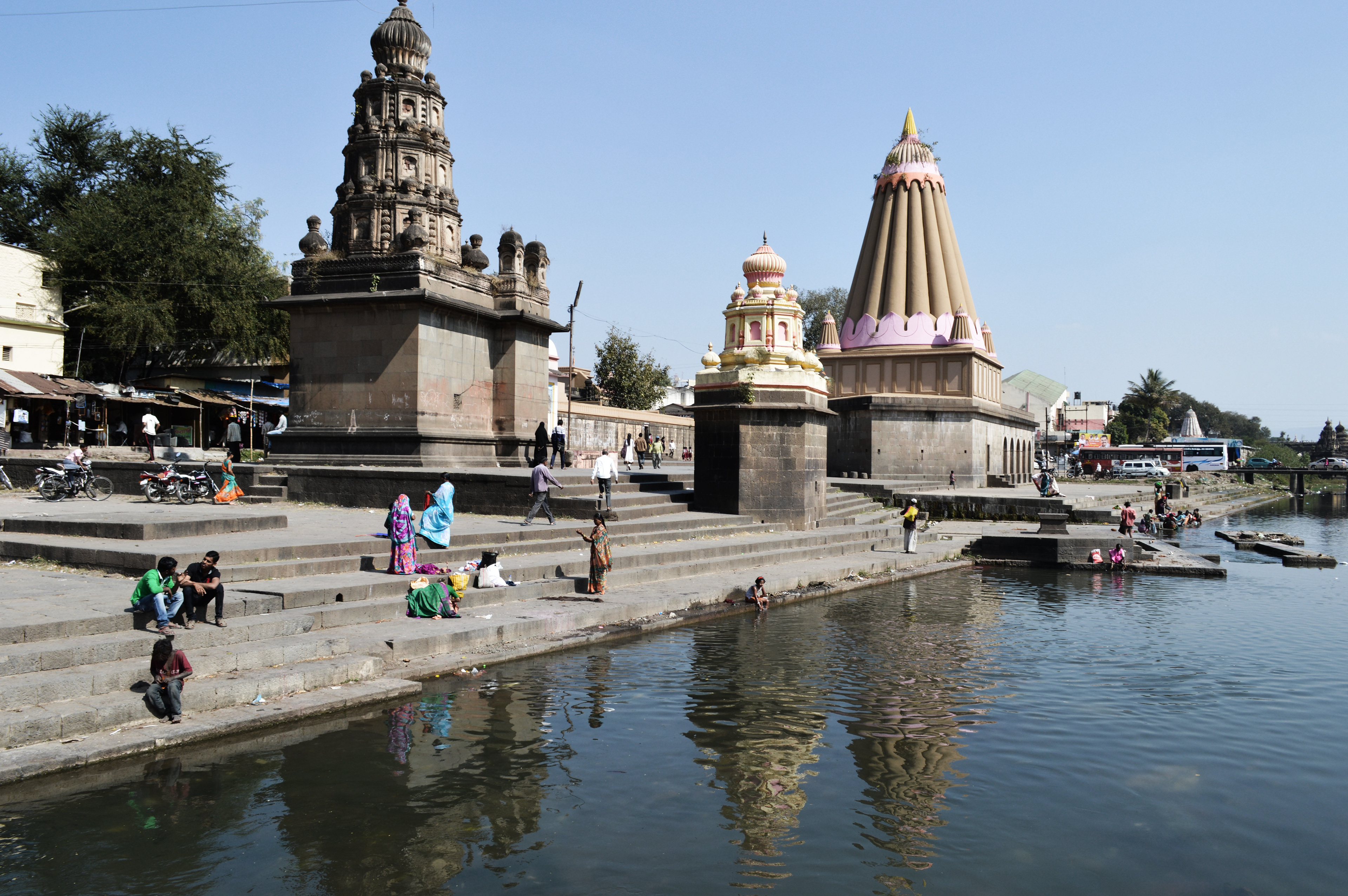
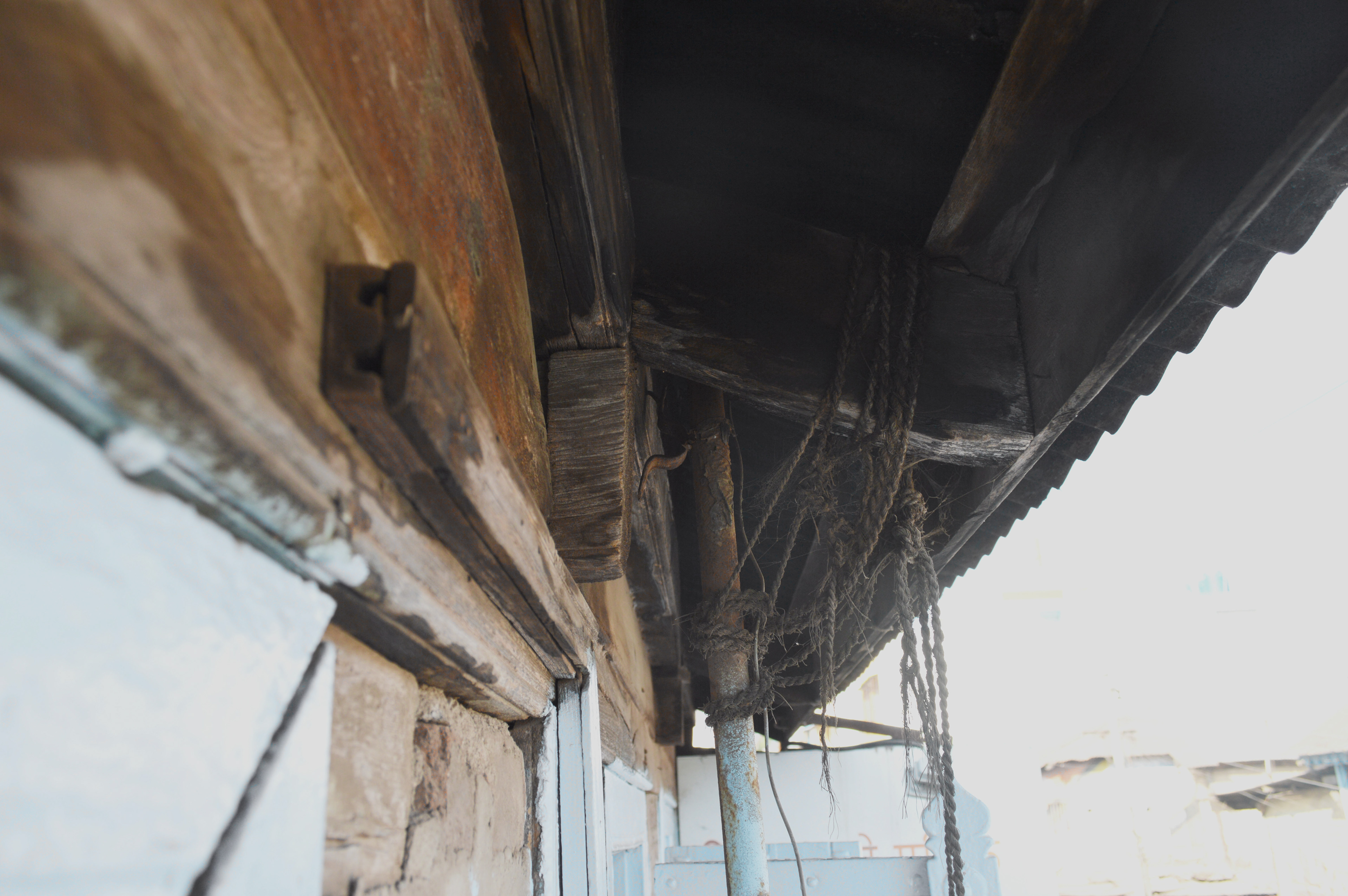
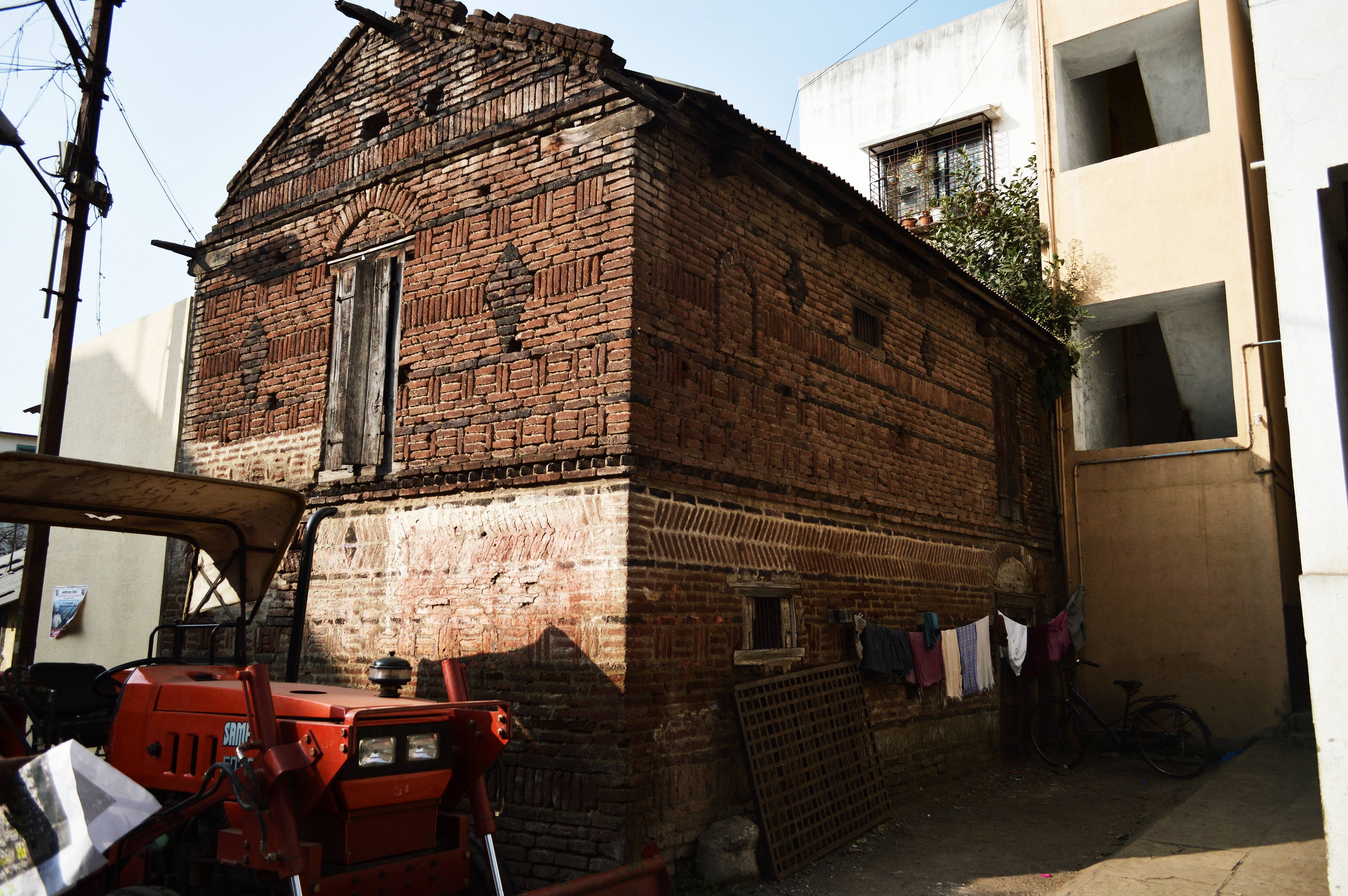




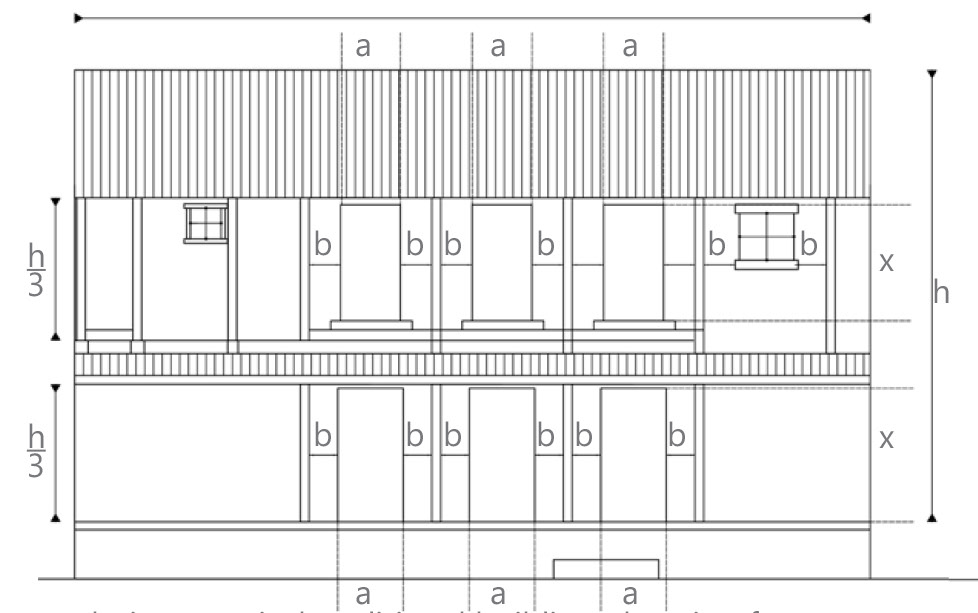
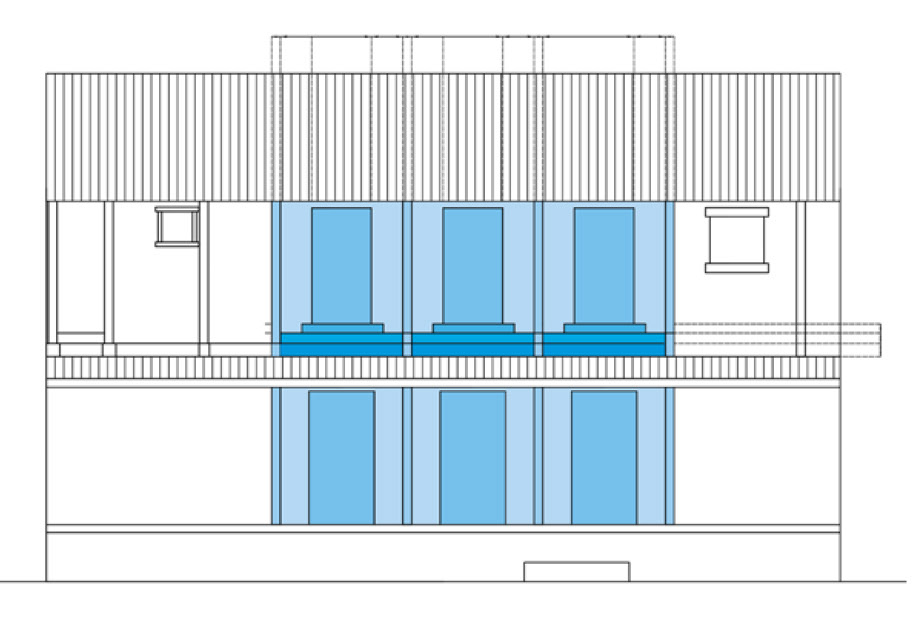
analyzing a typical traditional building elevation for
-rhythm of openings,
-proportions of solids and voids,
-frequency of materials and textures, and
-visual characteristics of each material and its relationships with neighboring materials.
-rhythm of openings,
-proportions of solids and voids,
-frequency of materials and textures, and
-visual characteristics of each material and its relationships with neighboring materials.
Analyzing a typical traditional wall section for
-structural,
-protective sacrificial, protective non sacrificial, and
-structural infill
properties of each element based on its specifications, visual language, texture and prominence in elevation.
-structural,
-protective sacrificial, protective non sacrificial, and
-structural infill
properties of each element based on its specifications, visual language, texture and prominence in elevation.
Steel Concrete Steel+RCC Glu-lam Timber
To maintain the traditional integrity and maintain a balance, only one material was replaced from the traditional wall section.
- steel is used as a structural member as truss to support long double height spans and in tandem with concrete.
- concrete is used as a structural and an infill material.
- vitrified floor tiles have been introduced as sacrificial material for open terraces.
- glu-lam timber is a direct replacement for traditionally used timber.
- steel is used as a structural member as truss to support long double height spans and in tandem with concrete.
- concrete is used as a structural and an infill material.
- vitrified floor tiles have been introduced as sacrificial material for open terraces.
- glu-lam timber is a direct replacement for traditionally used timber.
to ensure a successful long term result of contemporizing traditional architecture, a public-professional co-operative architectural research center has been proposed. the complex emulates the inherent relationship of the people with the river and as a model in itself by the use of modern materials such as concrete, steel, and laminated timber as direct functional replacements of their traditional counterparts.
A functional and characteristic analysis of traditional materials and their role in building elevations played key roles during the design process to produce functionally efficient contemporized architecture still reminiscent of the rich local heritage; the architectural research center allows the local population to exhibit their art and pass on their knowledge of design.
Despite a rich cultural and constructional heritage, new buildings are shifting further away from it and closer to a generic design language of contemporary times ignoring context and history.
setting up an architectural research center to explore, analyse and revitalize the indigenous construction systems would provide a chance at conserving the rich heritage of the region and an opportunity to the skilled native artisans of the town to express their skill in collaboration with professional research architects.
setting up an architectural research center to explore, analyse and revitalize the indigenous construction systems would provide a chance at conserving the rich heritage of the region and an opportunity to the skilled native artisans of the town to express their skill in collaboration with professional research architects.